- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping
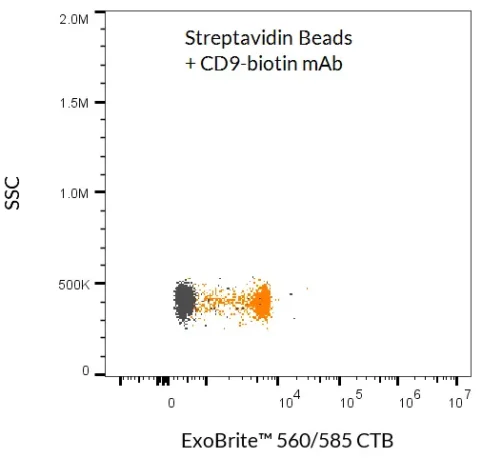
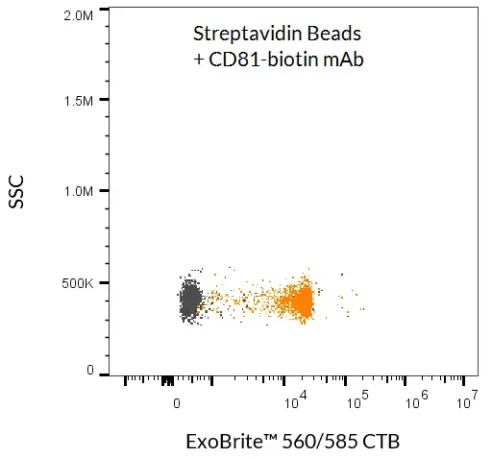
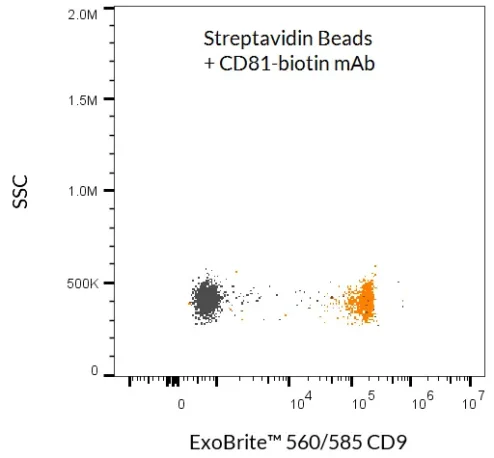
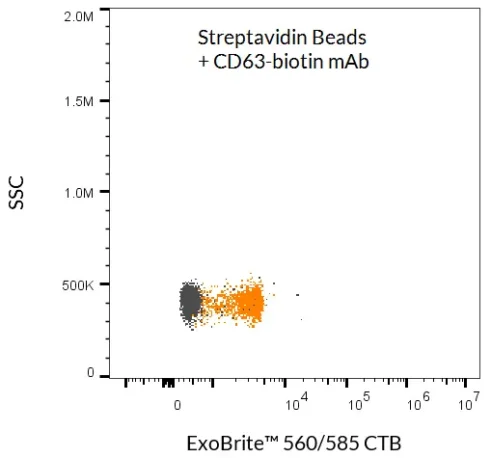
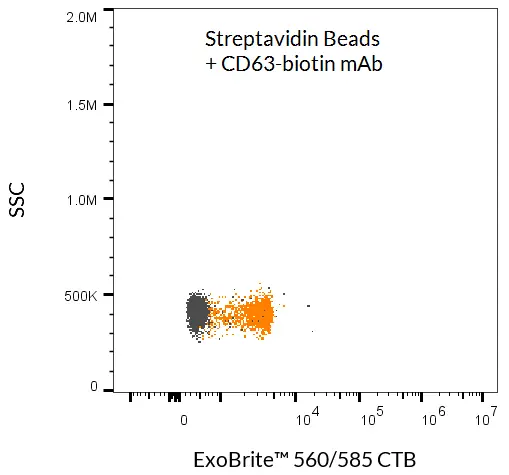
ExoBrite™ Streptavidin Magnetic Beads
ExoBrite™ Streptavidin Magnetic Beads are streptavidin-coated magnetic polystyrene beads (4.5 µm diameter) validated for the isolation of extracellular vesicles (EVs) and exosomes. When combined with a biotinylated antibody (not included), these beads provide a simple, efficient method for EV capture from cell culture medium or biological fluids without the need for an overnight precipitation step.
Designed for lower background and higher sensitivity compared to conventional methods, ExoBrite™ beads enable reliable EV isolation followed by downstream analysis with flow cytometry, fluorescence microscopy, or western blot. Bead-bound EVs can also be lysed for protein or nucleic acid analysis, supporting multi-modal EV characterisation.
Key Features
- Combine with a biotinylated antibody for EV capture
- Isolate EVs from biological fluids without precipitation
- Lower background, higher sensitivity than competitors
- Magnetic-based separation for speed and convenience
- Compatible with flow cytometry, microscopy, western blot, sequencing
Applications
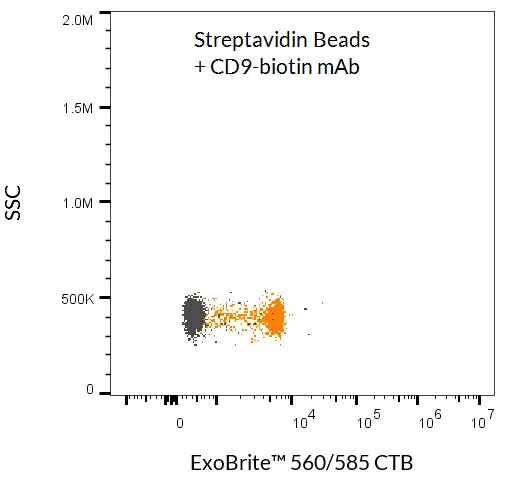
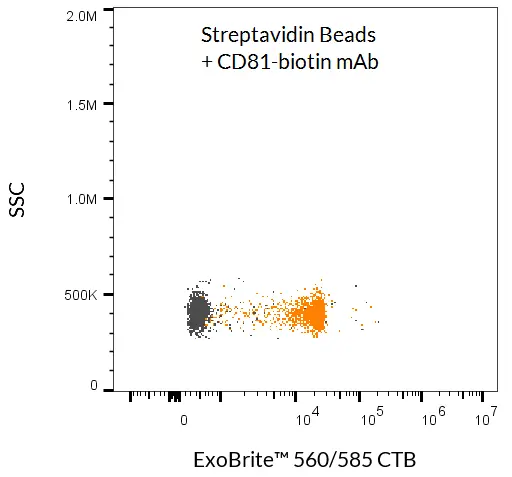
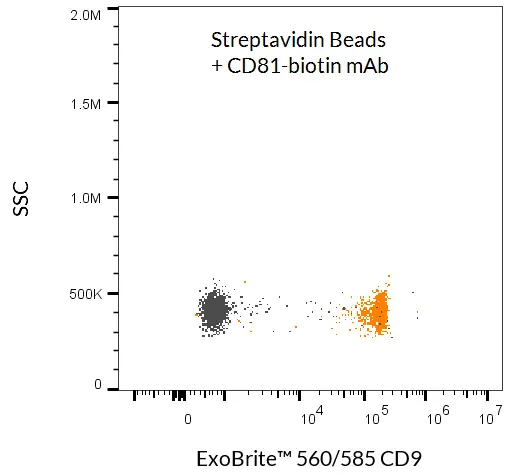
- EV/exosome isolation via antibody capture (CD9, CD63, CD81, or other membrane markers)
- Detection of bead-bound EVs with antibody conjugates or fluorescent probes
- Protein analysis by western blot
- Nucleic acid profiling by sequencing
Notes: Biotium products are available only in Singapore and Thailand.
Streamline your EV workflows with ExoBrite™ Streptavidin Magnetic Beads – high-sensitivity isolation without precipitation.
*Please leave us a message during checkout to indicate which kit you need, and our team will process your order accordingly.
Proven Performance