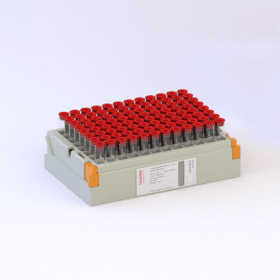
🔥 Don’t Miss Out on our Blind Box Giveaway with a minimum spend of $280!
🔥 Don’t Miss Out on our Blind Box Giveaway with a minimum spend of $280!
🔥 Don’t Miss Out on our Blind Box Giveaway with a minimum spend of $280!
🔥 Don’t Miss Out on our Blind Box Giveaway with a minimum spend of $280!
🔥 Don’t Miss Out on our Blind Box Giveaway with a minimum spend of $280!
🔥 Don’t Miss Out on our Blind Box Giveaway with a minimum spend of $280!